完成鸢尾花数据集后,突然发现还要求一个直观的Matplot展示,不得已,尝试捡起丢掉已久的matplot和numpy。
代码目标与架构思路
目标
将模型训练的结果直观化,形成一张彩色的图谱,图谱上有训练点和背景分区,当点的颜色和背景颜色不一致时,认为模型判断失误,否则模型预测成功。
思路
利用numpy生成一张500 * 500的数据矩阵作为背景,将其中的点全部通过模型预测( 需要重新训练只接受两个点的模型,因为一张二维图只有两个参数 ),并将显示结果通过不同颜色加以区分,形成色块,以此形成带颜色的背景。
再将真实值( 训练数据 )绘制成点标于其上即可。
涉及函数及参数简介
axis参数
用于指定对矩阵的堆砌和拆分遵循行还是列,有0和1两种指标。
meshgrid
用于形成网格,分别输入需要形成网格的横纵坐标集合,输出网格的两个坐标的矩阵形式。
上属:numpy
linspace
用于形成等差数组,输入依次为这个要形成的数组的最小值,最大值,数组元素个数,输出为数组。
上属:numpy
flat
用于将一个矩阵“扁平化”成一个数组,扁平化顺序一定。
上属:相应矩阵
stack
用于将两个大小相同的矩阵/或数组堆叠起来(axis参数为1时相当于取两个矩阵/数组位置相同的元素组合为一个坐标作为它新矩阵的元素)。输入为两个待处理矩阵和axis参数,输出为堆叠的矩阵。
上属:numpy
ListedColormap
用于形成后面上色的规则 cm( Colormap ),格式为输入[‘XX’,’XX’,’XX’],式中的XX表示颜色缩写或者具体编号,一般用RGB格式,其顺序就是上色顺序,因此数量和要上色的元素数量有关。输出为cm。
上属:matplotlib.colors
xlim(ylim)
设定显示的坐标轴范围,输入为(min,max),无输出。
上属:matplotlib.pyplot
pcolormesh
用于绘制分类背景,使得背景出现颜色。输入依次为需要构造的横纵坐标x1,x2,判定颜色的依据label,判定颜色的规则cmap = cm,无输出。
上属:matplotlib.pyplot
reshape
用于调整相应矩阵大小,输入为需要调整成的结果,同样是一个矩阵,由于是直接的下属函数,无输出。
上属:相应矩阵
scatter
用于绘制一连串有颜色的点作为标记点。输入依次为一串点的横纵坐标x1,x2,判定点的颜色的依据 c = label,判定点颜色的规则 cmap = cm,点的形状 maker, 点边缘颜色 edgecolors,无输出。
上属:matplotlib.pyplot
坐标轴的标签函数
xlabel/ylabel:设定xy轴名称。输入相应字符串,无输出。
title:设定图像名称。输入相应字符串,无输出。
上属皆为:matplotlib.pyplot
代码
贴上代码,里面已经有注释了,思路简单,故不再赘述。
1 | #绘图部分: |
加上完整的前后文后效果如下:
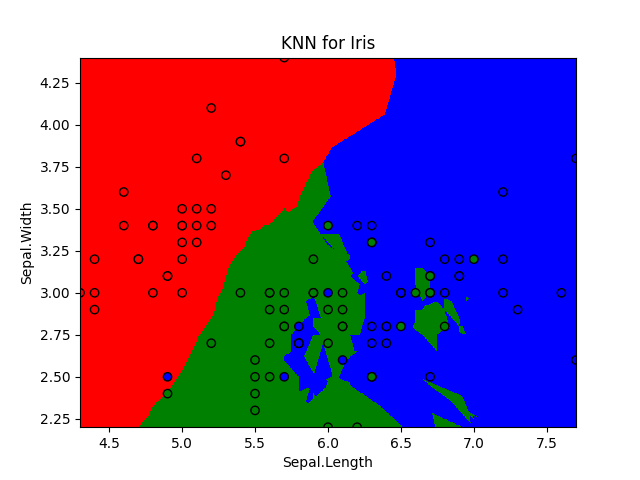
可以看到,效果还是很不错的,颜色不相同的地方就是模型判断失误的地方。
最后贴上完整代码:
1 | from sklearn import neighbors |
锵锵锵~完成